How to Install GRE Lamination Kits: Tools, Techniques, and Tips
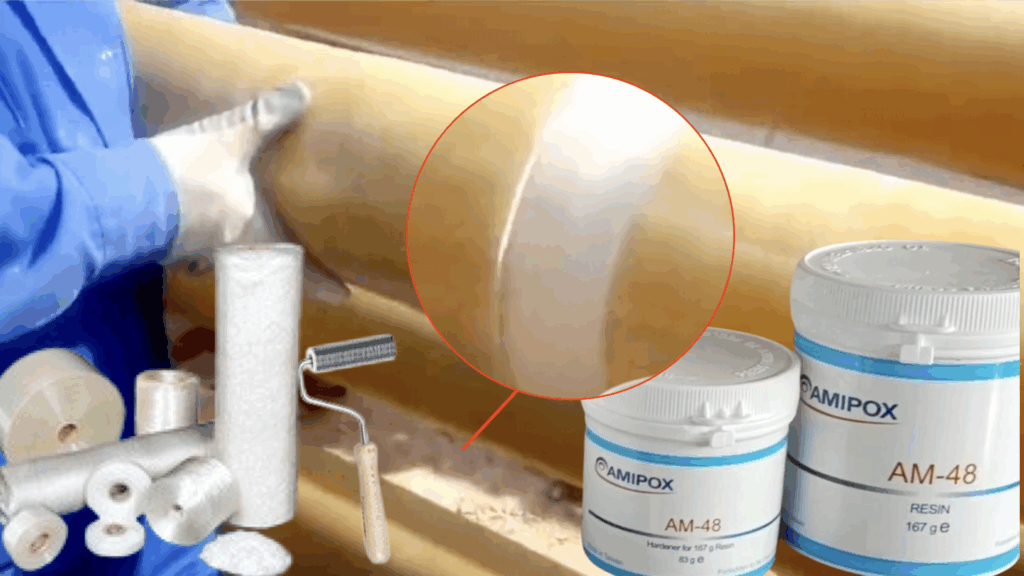

Glass Reinforced Epoxy (GRE) lamination kits are essential tools in industries that require corrosion-resistant, durable, and lightweight piping systems, particularly in oil & gas, marine, and chemical sectors. Whether you’re repairing a damaged pipe or joining new GRE components, proper GRE lamination tools techniques ensure strength, integrity, and long service life.
What is a GRE Lamination Kit?
A GRE lamination kit contains all the materials required for making structural joints or repairs on GRE pipes. The typical components include:
Epoxy Resin and Hardener: The bonding agent that holds everything together.
Glass Fiber Mat: Provides structural strength.
Mixing Container and Spatula: For preparing the epoxy.
Brush or Roller: For applying the resin evenly.
Gloves and Safety Gear: To protect the installer from chemicals.
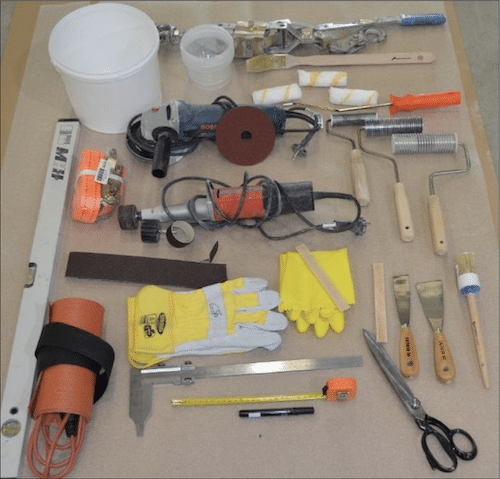

These kits are engineered for both field and factory applications, allowing technicians to perform reliable joints even under harsh conditions. GRE lamination tools techniques depend heavily on proper material selection and precise application. Equally important is safety. Installers must wear appropriate PPE (personal protective equipment) such as chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, coveralls, and a respirator or mask to protect against resin fumes and dust. You’ll also need consumables like epoxy resin systems with the correct hardener, glass fiber reinforcements (e.g., woven roving or chopped strand mat), peel ply, and acetone or other approved cleaning solvents. All materials should be stored in a clean, dry place and used within their shelf life.
Lamination Techniques: Butt and Adhesive Joints
The installation of GRE lamination kits primarily involves two types of joints: butt joints and adhesive (tapered) joints. Each method has its own application scenarios and technical requirements, but both demand careful attention to detail to ensure structural integrity. GRE lamination tools techniques are tailored based on the joint type and environmental conditions.
Butt Joint Lamination
The butt joint lamination technique is a widely used method for joining Glass Reinforced Epoxy (GRE) pipes. It involves the precise preparation and alignment of pipe ends, followed by the application of resin-impregnated fiberglass to form a strong, corrosion-resistant joint. This method is particularly effective in applications requiring high hoop strength and axial load resistance.

Process Overview:
-
Preparation:
Surface preparation includes grinding and thorough cleaning to ensure optimal bonding of the laminate material.
-
Fit-Up and Alignment:
Pipe ends are aligned along a common centerline, maintaining a specified gap (typically around 3 mm). Temporary supports or fixtures are used to hold the pipes securely in position during lamination.

-
Lamination:
The lamination process involves the use of resin and fiberglass materials, such as chopped strand mat or multi-axial glass fiber mat combined with the appropriate hardener and catalyst.
Before applying the laminate, the joint area is filled with putty to eliminate irregularities and provide a smooth, uniform surface. Layers of fiberglass, saturated with resin, are then applied to the joint. Each layer is thoroughly wetted and rolled to eliminate air pockets and ensure full adhesion.
The number of layers and choice of reinforcement materials depend on factors such as pipe diameter, pressure rating, and the specific application requirements. These steps reflect critical GRE lamination tools techniques for structural performance.
4. Curing:
Once lamination is complete, the joint is left to cure, allowing the materials to bond and form a strong, monolithic connection between the pipes. Curing may be accelerated by regulating environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity.
-
Quality Control:
Throughout the fit-up and lamination process, inspection by a qualified professional is essential. The joint must be thoroughly assessed to ensure it meets all required specifications and performance standards.
Key Advantages of the Butt Joint:
- Delivers high strength with excellent resistance to internal pressure and axial loads.
- Versatile across a wide range of pipe diameters and pressure classes.
- Provides strong corrosion resistance, extending service life in demanding environments.
Adhesive Joint Lamination
Laminating adhesive joints in GRE (Glass Reinforced Epoxy) and GRP (Glass Reinforced Polyester) piping systems is a critical process, essential for ensuring joint integrity and system reliability. The process typically involves preparing the pipe surfaces, mixing the adhesive, applying it to the joint, and then curing the joint, often with the aid of a heating pad. This method reflects specialized GRE lamination tools techniques tailored for chemical bonding.
Adhesive bonding forms a chemically sealed and mechanically reinforced joint, providing leak resistance, structural strength, and long-term durability.
Process Overview:
Surface Preparation: Surface preparation begins with thoroughly cleaning the spigot and socket ends of the pipes to ensure they are clean, dry, and free of grease and dust. A suitable solvent should be used to remove any residual substances. For tapered joints, the spigot end must be precisely shaved to the correct angle and diameter using a specialized fiberglass pipe shaver, ensuring a tight, uniform fit.
Adhesive Application: The mixed adhesive is applied evenly to the prepared pipe ends, depending on the joint design and configuration.
Joint Assembly: The pipes are brought together with precise alignment, ensuring full engagement and even adhesive distribution across the bonding surface.
Curing: A heating blanket or other heat source may be used to accelerate the curing process. Curing time can vary but often requires several hours to achieve full bond strength.
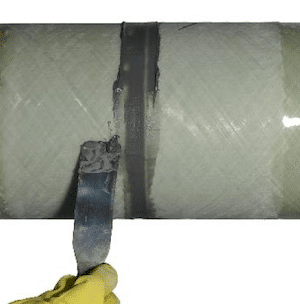
Key Advantages of Adhesive Bonding and OTA Fiberglass Adhesive:
- Provides excellent corrosion and chemical resistance, especially in offshore or industrial environments.
- Compatible with a wide range of GRE pipe diameters and configurations.
- Strong, continuous bonding with excellent leak resistance and mechanical integrity.
- Works with various pipes from different manufacturers
For detailed specifications and technical guidance on adhesive preparation and application, please refer to the following datasheet.
document: OTA Fiberglass Adhesive Product Datasheet (PDF)
In adhesive joint applications, we use Pipe Shaver and Heating Blankets to prepare and cure pipe joints. Let us see more about OTA Fiberglass Pipe Shaver and OTA Fiberglass Heating Blanket and how we use OTA Fiberglass products for effective bonding below.
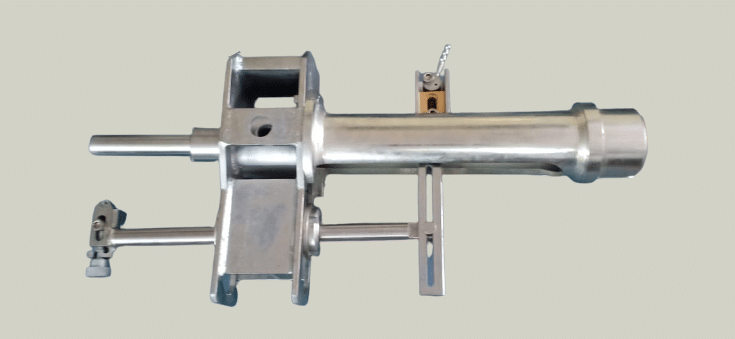
OTA Fiberglass Pipe Shaver is a precision-engineered tool designed for uniform tapering and surface preparation of spigot ends in GRE and GRP piping systems. This professional-grade machine ensures accurate and consistent shaving at the correct angle, which is essential for achieving high-quality adhesive joints.
- Designed for use with GRE and GRP pipes.
- Accommodates multiple pipe sizes with a single unit.
- Fully compatible with major pipe manufacturer specifications.
- High-precision blade assembly delivers smooth, even surface finish.
- Adjustable cutting depth to suit various pipe diameters and wall thicknesses.
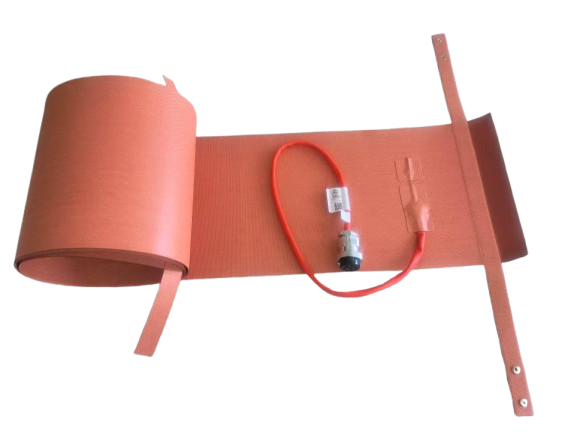
OTA Fiberglass Heating Blanket is a high-performance curing solution specifically designed for adhesive joint applications in GRE and GRP piping systems. It ensures precise, uniform heat distribution throughout the curing process, promoting strong adhesive bonds and long-term joint reliability. Used in curing RTR pipes post lamination as shown above.
- Delivers consistent and even heat across the joint area, preventing hotspots and ensuring uniform curing.
- Adjustable temperature control to meet the specific curing requirements of various adhesive systems.
- Lightweight and flexible construction allows for quick wrapping and a secure fit on different pipe diameters.
- Integrated power and heater-on neon indicators for clear and convenient operation monitoring.
- Supports curing temperatures up to 200°C, ideal for field and workshop applications.
Best Practices and Pro Tips
Even with the right tools and a sound understanding of lamination techniques, successful GRE joint installation depends on a number of critical best practices that can make or break the job. Proper application of GRE lamination tools techniques can significantly impact the quality of the final joint.
First, environmental control is key. Resin systems are sensitive to humidity and temperature, and improper curing conditions can lead to weak or brittle joints.
During lamination, remember to remove air bubbles between layers using a bubble roller. Air pockets reduce the strength and durability of the joint. Work methodically and allow proper curing between layers if doing multi-stage lamination.
It’s also important to strictly follow the resin mixing ratios. Chemical imbalance may lead to incomplete curing or compromised joint strength. Always use calibrated measuring tools.
Conclusion:
Proper GRE lamination requires the right technique, materials, and tools to ensure strong, durable, and leak-free joints. Whether you’re applying butt or adhesive joints, precision and care are key to long-term performance. Mastery of GRE lamination tools techniques leads to consistent, high-performance outcomes in the field.
OTA Fiberglass Engineering supports this mission by providing high-quality tools like the Pipe Shaver and Heating Blanket, designed to enhance accuracy, safety, and efficiency in the field. With a focus on innovation and reliability, OTA is dedicated to helping industries build better, longer-lasting GRE piping systems.

Learn More About Us
Reengineer Value

